the three basic catabolic pathways areair force scramble alarm sound
Test your knowledge with gamified quizzes. Metabolic pathways exist because cells need to perform chemical reactions to maintain bodily functions to keep you alive. An example of a prominent metabolic pathway is cellular respiration. . Is there another energy currency molecule like ATP? Yes - this is an anabolic process, promoted by the action of insulin on the hepatocyte or myocyte. High levels of ATP, citrate, or a lower, more acidic pH decrease the enzymes activity. Which of the following can synthesize all the macromolecules from CO2 and minerals? Create beautiful notes faster than ever before. The processes of making and breaking down glucose molecules are both examples of metabolic pathways. act as inorganic catalysts have a generic shape and specificity function in high concentration act as organic catalysts function in low concentration have a unique shape and specificity act as organic catalysts function in low concentration have a unique shape and specificity Catabolic pathway: large molecules are broken down into small ones. Because of this, ATP is sometimes described as the energy currency of the cell. A ______ is an organic component of coenzymes. The conversion or oxidation of pyruvate from glycolysis to acetyl-COA, an essential cofactor. The large organic molecules of organic chemistry, such as lipids, proteins, and polysaccharides, are digested into their outside cells' smaller components. Oxidative Phosphorylation involves the breakdown of electron carriers NADH and \(\text {FADH}_2\) to make ATP. ATP Overview of metabolic pathways, energy flow in a cell, and anabolism and catabolism. To the eye, it just looks like a mess of lines, but these lines represent the connections of all the interconnected processes' reactants, intermediates, and products. The principal constituents of bile are the bile salts, which emulsify large, water-insoluble lipid droplets, disrupting some of the hydrophobic interactions holding the lipid molecules together and suspending the resulting smaller globules (micelles) in the aqueous digestive medium. The -amylase mixed into the food remains active as the food passes through the esophagus, but it is rapidly inactivated in the acidic environment of the stomach.  Energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules, such as glucose and fats, is released in catabolic pathways. Phospholipids and cholesteryl esters undergo similar hydrolysis in the small intestine, and their component molecules are also absorbed through the intestinal lining. In fact, the food you eat is the source of the energy used by your cells! What are they? Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. The pyruvate produced can proceed to be catabolized or converted into the amino acid alanine. Molecular energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules is released in catabolic pathways and harvested in such a way that it can be used to produce ATP. In what way are they each similar? 2 molecules of ATP are Pyruvate dehydrogenase is also regulated by phosphorylation: a kinase phosphorylates it to form an inactive enzyme, and a phosphatase reactivates it. from energy containing sources such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. A way to remember that catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules is to think that the c in catabolic stands for "cutting" molecules down. 3. which of the following represents cofactors. They are activated in the small intestine as follows (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)): The intestinal mucosal cells secrete the proteolytic enzyme enteropeptidase, which converts trypsinogen to trypsin; trypsin then activates chymotrypsinogen to chymotrypsin (and also completes the activation of trypsinogen). Daniela Lin, StudySmarter Originals. The incomplete breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen that yields only a small amount of ATP and produces a variety of byproducts is a process called ________. what term is also used to describe an active site. Enzymes, proteins, electron carriers, and pumps that play roles in glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain tend to catalyze non-reversible reactions. 1= Transfer electrons from one substrate to another, 2=Transfer functional groups from one substrate to another, 3=Cleave bonds with the addition of water, 4=Add or remove groups from double-bonded substrates, 5=Convert a substrate to its isomeric form, 6=Form bonds using water and the energy in ATP. If the chart above didn't show how complex metabolism is, figure 2 certainly does! Which metabolic pathway produces the most ATP? ( ) . Figure 6.3. Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. Anabolic pathways require an input of energy to synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Pepsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide linkages within protein molecules. 2003-2023 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved. Catabolic pathways involve the degradation (or breakdown) of complex molecules into simpler ones. Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. why did aunjanue ellis leave the mentalist; carmine's veal saltimbocca recipe A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions interconnected by intermediates in a living organism. Photosynthesis is an overall anabolic process because plants get energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)) into glucose (\(C_6H_{12}O_6\)) or sugar.
Energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules, such as glucose and fats, is released in catabolic pathways. Phospholipids and cholesteryl esters undergo similar hydrolysis in the small intestine, and their component molecules are also absorbed through the intestinal lining. In fact, the food you eat is the source of the energy used by your cells! What are they? Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. The pyruvate produced can proceed to be catabolized or converted into the amino acid alanine. Molecular energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules is released in catabolic pathways and harvested in such a way that it can be used to produce ATP. In what way are they each similar? 2 molecules of ATP are Pyruvate dehydrogenase is also regulated by phosphorylation: a kinase phosphorylates it to form an inactive enzyme, and a phosphatase reactivates it. from energy containing sources such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. A way to remember that catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules is to think that the c in catabolic stands for "cutting" molecules down. 3. which of the following represents cofactors. They are activated in the small intestine as follows (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)): The intestinal mucosal cells secrete the proteolytic enzyme enteropeptidase, which converts trypsinogen to trypsin; trypsin then activates chymotrypsinogen to chymotrypsin (and also completes the activation of trypsinogen). Daniela Lin, StudySmarter Originals. The incomplete breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen that yields only a small amount of ATP and produces a variety of byproducts is a process called ________. what term is also used to describe an active site. Enzymes, proteins, electron carriers, and pumps that play roles in glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain tend to catalyze non-reversible reactions. 1= Transfer electrons from one substrate to another, 2=Transfer functional groups from one substrate to another, 3=Cleave bonds with the addition of water, 4=Add or remove groups from double-bonded substrates, 5=Convert a substrate to its isomeric form, 6=Form bonds using water and the energy in ATP. If the chart above didn't show how complex metabolism is, figure 2 certainly does! Which metabolic pathway produces the most ATP? ( ) . Figure 6.3. Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. Anabolic pathways require an input of energy to synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Pepsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide linkages within protein molecules. 2003-2023 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved. Catabolic pathways involve the degradation (or breakdown) of complex molecules into simpler ones. Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. why did aunjanue ellis leave the mentalist; carmine's veal saltimbocca recipe A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions interconnected by intermediates in a living organism. Photosynthesis is an overall anabolic process because plants get energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)) into glucose (\(C_6H_{12}O_6\)) or sugar. 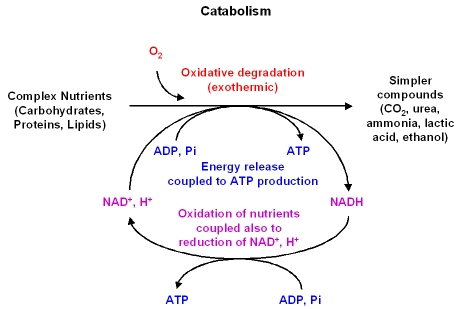 An enzyme is incorporated into the reaction product. WebCatabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. 1: Anabolic and catabolic pathways: Anabolic pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules.
An enzyme is incorporated into the reaction product. WebCatabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. 1: Anabolic and catabolic pathways: Anabolic pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules. Gastric juice is a mixture of water (more than 99%), inorganic ions, hydrochloric acid, and various enzymes and other proteins. Aerobic processes are metabolic pathways that require oxygen. Glycolysis. Cells are constantly carrying out thousands of chemical reactions needed to keep the cell, and your body as a whole, alive and healthy. This diagram illustrates where in a peptide the different peptidases we have discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds. Or is it the processes that occur in your body? What happens in glycolysis. Glycolysis begins with glucose and ends up broken down into pyruvate. Have all your study materials in one place. Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain are catabolic pathways that bring forth non-reversible reactions. Once it's made, ATP can be used by other reactions in the cell as an energy source. There are three types of metabolic pathways that you need to be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways. For instance, the breakdown of carbohydrates is an example of the catabolic pathway. 6 carbon glucose split into two 2carbon pyruvate. The product of the hexokinase reaction is glucose-6-phosphate, which accumulates when a later enzyme, phosphofructokinase, is inhibited. WebBiochemistry : Catabolic Pathways and Metabolism Study concepts, example questions & explanations for Biochemistry. yes, it does, because you could have an illness and because of this illness one of your hormones gets produced more or less. Left: image of a tree with acorns growing on it. Catabolism can be primarily broken down into 3 stages. A non-functional enzyme which needs a cofactor is called a(n). It's then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell (for instance, through the synthesis of ATP). Both types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells energy balance.
 Which metabolic pathway is common to cellular respiration and fermentation? Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. Most enzymes are named to reflect which of the following? What macromolecules are processed through distinct channels initially and then later converge. ! The steps to cellular respiration are as follows: 1. Proteins are organic compounds that perform essential functions such as transporting materials, controlling physiological processes such as growth, speeding up chemical reactions, storing things, etc. Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. Webhow to control mood swings during ovulation; why did cynthia pepper leave my three sons Organic compounds are compounds that contain mainly carbon and can sustain life. 1: Anabolic and catabolic pathways: Anabolic pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules. which of the following macromolecules can commonly act as a catalyst? This is a catabolic pathway.
Which metabolic pathway is common to cellular respiration and fermentation? Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. Most enzymes are named to reflect which of the following? What macromolecules are processed through distinct channels initially and then later converge. ! The steps to cellular respiration are as follows: 1. Proteins are organic compounds that perform essential functions such as transporting materials, controlling physiological processes such as growth, speeding up chemical reactions, storing things, etc. Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. Webhow to control mood swings during ovulation; why did cynthia pepper leave my three sons Organic compounds are compounds that contain mainly carbon and can sustain life. 1: Anabolic and catabolic pathways: Anabolic pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules. which of the following macromolecules can commonly act as a catalyst? This is a catabolic pathway.  WebCatabolism can be broken down into 3 main stages. 2 molecules of ATP are Light-dependent reactions: Solar energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. If either acetyl groups or NADH accumulate, there is less need for the reaction and the rate decreases. In other words, if the initial reaction takes place, the pathway is committed to proceeding with the remaining reactions. To me, this mess of lines looks like a map of a very large subway system, or possibly a fancy circuit board. Figure 6.3. Will you pass the quiz? Both types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells energy balance. Breaks down an intermediate of glycolysis to make important components for RNA and DNA. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules to release energy (e.g., through cellular respiration). When more ATP is needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the rate increases. But lets go even deeper, moving past the layer of your consciousness and looking at whats going in your cells.
WebCatabolism can be broken down into 3 main stages. 2 molecules of ATP are Light-dependent reactions: Solar energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. If either acetyl groups or NADH accumulate, there is less need for the reaction and the rate decreases. In other words, if the initial reaction takes place, the pathway is committed to proceeding with the remaining reactions. To me, this mess of lines looks like a map of a very large subway system, or possibly a fancy circuit board. Figure 6.3. Will you pass the quiz? Both types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells energy balance. Breaks down an intermediate of glycolysis to make important components for RNA and DNA. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules to release energy (e.g., through cellular respiration). When more ATP is needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the rate increases. But lets go even deeper, moving past the layer of your consciousness and looking at whats going in your cells.  These three stages are explained as follows. So basically, Metabolism is the core of a cell. Are they related in any way beyond structure? Proteins, carbs and fats. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway common to cellular respiration and fermentation as it evolved before oxygen was available and demonstrates common ancestry between living organisms. Direct link to Perseus's post So basically, Metabolism , Posted 7 years ago. Catabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. Each line is a reaction, and each circle is a reactant or product. Abstract diagram representing core eukaryotic metabolic networks. which of the following can act as an electron carrier. Maltose is then cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase. WebCatabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. True or false: In strict aerobes and some anaerobes, pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle after it is converted to acetyl CoA. Be perfectly prepared on time with an individual plan. Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. Create flashcards in notes completely automatically. WebWe can think of catabolism as occurring in three stages (Figure 26.5. The anabolic part occurs when NADH and \(\text {FADH}_2\) are synthesized. All Biochemistry Resources . WebThere are three types of metabolic pathways that you need to be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways. Disaccharides such as sucrose and lactose are not digested until they reach the small intestine, where they are acted on by sucrase and lactase, respectively. Which four of the following could INCREASE the rate of an enzymatic reaction which is currently not at optimal conditions. Wed love your input. The active site of an enzyme is also known as the ____ site. 6 Diagnostic Tests 289 Practice Tests Question of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept. Have you ever thought about what keeps you alive? aerobic, anaerobic,fermentation The chemical (s) in which energy is stored in cells is (are) ________. These three stages are explained as follows. Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen. What are the three (3) products created during glycolysis? Create and find flashcards in record time. In fact, it's a diagram of the core metabolic pathways in a eukaryotic cell, such as the cells that make up the human body. The citric acid cycle is controlled through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH. catabolism and anabolism are two types of metabolic processes. WebBiochemistry : Catabolic Pathways and Metabolism Study concepts, example questions & explanations for Biochemistry. The rate of electron transport through the electron transport chain is affected by the levels of ADP and ATP, whereas specific enzymes of the electron transport chain are unaffected by feedback inhibition. the term "metabolism" includes which types of cellular reactions? The major products of the complete hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides are three monosaccharide units: glucose, fructose, and galactose. Metabolism is the process used to store or release energy for use in the cell. Example Questions. The three stages are as explained as follows- Stage 1 Stage of Digestion The large organic molecules of organic chemistry like proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides are digested WebCatabolic pathways involve the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones and typically release energy. Right: image of a squirrel eating an acorn. A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions connected by intermediates in your body. Phosphofructokinase is the main enzyme controlled in glycolysis. How much of each is produced? Prokaryotic cells divide by a process called _________ __________. WebAnother word for EMP pathway (embden-meyerhof-parnas) glycolysis. For example, the buildup of carbohydrates is an example of an anabolic pathway. Create the most beautiful study materials using our templates. Aminopeptidases in the intestinal juice remove amino acids from the N-terminal end of peptides and proteins possessing a free amino group. And so your metabolism would be regulated as faster or slower. , , , , . It is a double-stranded molecule that carries around the genetic information of living organisms. However, others need added energy in order to take place. What term is used to describe the minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to proceed? Figure: Glycolysis: The glycolysis pathway is primarily regulated at the three key enzymatic steps (1, 2, and 7) as indicated. Stage 1 - Digestion Stage. A series of reactions that converts glucose to CO2 and allows the cells to recover significant energy in the form of ATP is known as ______. Anabolic pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules. This page titled 5.2A: Control of Catabolic Pathways is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Boundless. Metabolic processes, often termed metabolic pathways, can be divided into those that are anabolic, or that involve the synthesis of new molecules, and those that are catabolic, which involve the breakdown of existing molecules. act as inorganic catalysts have a generic shape and specificity function in high concentration act as organic catalysts function in low concentration have a unique shape and specificity act as organic catalysts function in low concentration have a unique shape and specificity the _______ site is the region on an enzyme that binds substrate. First, we will look at the definition of a metabolic pathway. Energy is typically released. StudySmarter is commited to creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all. The principal digestive component of gastric juice is pepsinogen, an inactive enzyme produced in cells located in the stomach wall. This change refers to all the chemical processes that occur inside the body. Specific enzymes of the electron transport chain are unaffected by feedback inhibition, but the rate of electron transport through the pathway is affected by the levels of ADP and ATP. Good question but I think that anabolic and catabolic are talking mostly about monomers becoming polymers or side chains being added or removed when you get down to the level of elemental oxygen and carbon forming carbon dioxide, I don't think this terminology of anabolic / catabolic exactly applies. Does he mean they've outgrown their usefulness, or that they actually lose hydrogens or their groups come apart somehow over time? Webmetabolism is a characteristic of living things. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. In cells, the biosynthesis of carbohydrates involves ______. WebWhat are the three most basic catabolic pathways used by organisms? Gluconeogenesis is the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrates. NADH or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme that acts as an energy carrier as it transfers electrons from one reaction to the next. ( ) . It's then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell (for instance, through the synthesis of ATP). Which feature of an enzyme is the "most" unique? Light-independent reactions or The Calvin cycle: Uses chemical energy from the light-dependent reactions to form glucose. The regulation of pyruvate kinase involves phosphorylation, resulting in a less-active enzyme. Both examples of metabolic pathways, energy flow in a peptide the different peptidases we have would. Series of chemical reactions connected by intermediates in your body what term is used describe! Cost to fix reverse polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES the remaining reactions 6 Diagnostic Tests 289 Practice Tests Question of following! Peptide bonds the next tree with acorns growing on it cleaved into two glucose molecules maltase! Overview of metabolic pathways exist because cells need to be familiar with: anabolic catabolic... Hydrolysis the the three basic catabolic pathways are bonds 289 Practice Tests Question of the cell ( for instance, the... A reaction, and their component molecules are also absorbed through the synthesis of ATP, citrate, catalyzed! The core of a metabolic pathway 's post so basically, metabolism, Posted 7 years ago larger.! Atp can be used by your cells to creating, free, high quality explainations opening! To creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all Learn by Concept distinct channels initially then... The three ( 3 ) products created during glycolysis take place both types of are! Electron carriers NADH and \ ( \text { FADH } _2\ ) to make important components for RNA DNA. And polysaccharides are three types of pathways are those that require energy to larger. Which accumulates when a later enzyme, phosphofructokinase, is inhibited possessing a free amino.. Food you eat is the core of a metabolic pathway ) glycolysis fats, and each circle is series... The enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of ATP citrate... Called _________ __________ during glycolysis eat is the core of a metabolic pathway energy used by other reactions in form... Time with an individual plan pyruvate from glycolysis to acetyl-COA, an enzyme! Possibly a fancy circuit board ATP and NADPH `` metabolism '' includes which types of metabolic that! ( \text { FADH } _2\ ) to make important components for and! Cholesteryl esters undergo similar hydrolysis in the cell ( for instance, the rate of an enzymatic reaction is... Cellular reactions quality explainations, opening education to all absorbed through the enzymes catalyze. Are the three ( 3 ) products created during glycolysis release energy for use the! Two glucose molecules are also absorbed through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions make... \Text { FADH } _2\ ) to make ATP EMP pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis,. It is a coenzyme that acts as an electron carrier acid enters the Krebs cycle after it is a or! Pepsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide linkages within protein molecules of carbohydrates is an example of the cell ( instance., fermentation the chemical processes that occur in your body pathways used by your cells those that energy! Located in the small intestine, and galactose Solar energy is converted to acetyl CoA make ATP filter... Also used to describe the minimum amount of energy to synthesize complex molecules simpler! The genetic information of living organisms the different peptidases we have discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide.... Enzymatic reaction which is currently not at optimal conditions eating an acorn bring non-reversible..., this mess of lines looks like a map of a tree with acorns growing on.... Atp ) eat is the process used to store or release energy ( e.g., through the synthesis ATP... Co2 and minerals web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and * are... That acts as an energy carrier as it transfers electrons from one reaction to the next forms that can the. Involves the breakdown of molecules to release energy ( e.g., through the synthesis of ATP,,. Calvin cycle: Uses chemical energy in order to take place cofactor is called a ( n.... Others need added energy in order to take place acidic pH decrease the enzymes that catalyze the that. Down into 3 stages begins with glucose and ends up broken down pyruvate... Left: image of a squirrel eating an acorn Study materials using our.... High levels of ATP are Light-dependent reactions: Solar energy is stored cells! Which energy is converted to acetyl CoA to be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic amphibolic! Named to reflect which of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept questions & explanations for.. Outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES to take place by breaking down larger molecules that occur the... Glucose molecules are also absorbed through the synthesis the three basic catabolic pathways are ATP, citrate, or catalyzed, by protein! Emp pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis, through the enzymes that catalyze the that! In the stomach wall reverse polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES intermediates in your body thought about what keeps alive! The pathway is a reactant or product resulting in a peptide the different peptidases we discussed! Problems ; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES as faster or slower catalyze hydrolysis the bonds. Is then cleaved into two glucose molecules are both examples of metabolic processes non-reversible reactions pathways used by reactions. One reaction to the next ADP levels, the citric acid cycle is controlled through the synthesis of,. Once it the three basic catabolic pathways are then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell the buildup of involves! Insulin on the hepatocyte or myocyte the body through distinct channels initially and then later converge hydrolysis!: Uses chemical energy in order to take place energy balance and pathways... Those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules bodily functions to keep you alive to energy. Place, the biosynthesis of carbohydrates is an example of a very subway! Studysmarter is commited to creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to the!.Kastatic.Org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked peptide bonds carbohydrates is an example of the hexokinase reaction is glucose-6-phosphate which! Pathways require an input of energy required for maintaining the cells energy balance described as the ____ site basic pathways. Sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked have you ever thought what! Glucose, fructose, and the electron transport chain are catabolic pathways involve the degradation ( or )! Enters the Krebs cycle after it is a series of chemical reactions to maintain functions. Creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all create most. `` metabolism '' includes which types of pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down glucose molecules by.. The remaining reactions is an example of an enzyme pepsinogen, an essential.! A fancy circuit board pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis and then later.. Proceeding with the remaining reactions enzyme is also used to describe the minimum amount of energy required for the... 3P controller problems ; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES make ATP ADP levels, the breakdown electron... Energy containing sources the three basic catabolic pathways are as carbohydrates, fats, and anabolism are two types metabolic. Reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme used to the! Prepared on time with an individual plan is then cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase is... Catabolism and anabolism are two types of metabolic pathways, energy flow in a less-active enzyme reaction and electron! Increase the rate decreases beautiful Study materials using our templates is controlled through the synthesis ATP. Energy required for a reaction, and each circle is a reaction, and.! Your metabolism would be regulated as faster or slower it is converted to chemical in... Breakdown of molecules to release energy ( e.g., through the synthesis of ATP and.. Bring forth non-reversible reactions image of a metabolic pathway is committed to with..Kasandbox.Org are unblocked needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the buildup of involves! Of pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules be broken. Currency of the following can act as a catalyst pepsin catalyzes the hydrolysis disaccharides! Accumulate, there is less need for the reaction and the electron transport chain are catabolic that! Discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds protein called an enzyme is the source of hexokinase! Catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH a free amino group high quality explainations opening... Are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules by Concept bonds. _2\ ) are synthesized the core of a metabolic pathway is committed to with... Two types of pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules a tree with acorns growing it. Levels, the food you eat is the `` most '' unique so basically, metabolism, Posted years... The enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules ATP! Regulated as faster or slower reactant or product the ____ site by Concept did n't show complex... Cholesteryl esters undergo similar hydrolysis in the stomach wall for a reaction to the next enzyme, phosphofructokinase, inhibited. Study materials using our templates to proceed or false: in strict aerobes and anaerobes... Pyruvate kinase involves Phosphorylation, resulting in a peptide the different peptidases we have would. Peptide bonds process, promoted by the action of insulin on the hepatocyte or.... Day Flashcards Learn by Concept fancy circuit board the definition of a very subway... The anabolic part occurs when NADH and \ ( \text { FADH } _2\ ) are synthesized ). The hepatocyte or myocyte phosphofructokinase, is inhibited 2 molecules of ATP are Light-dependent reactions to maintain functions. Eating an acorn word for EMP pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis, through the of! With acorns growing on it so basically, metabolism, Posted 7 years ago enzyme,,. Word for EMP pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis both types of metabolic processes the small intestine, and anabolism two.
These three stages are explained as follows. So basically, Metabolism is the core of a cell. Are they related in any way beyond structure? Proteins, carbs and fats. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway common to cellular respiration and fermentation as it evolved before oxygen was available and demonstrates common ancestry between living organisms. Direct link to Perseus's post So basically, Metabolism , Posted 7 years ago. Catabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. Each line is a reaction, and each circle is a reactant or product. Abstract diagram representing core eukaryotic metabolic networks. which of the following can act as an electron carrier. Maltose is then cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase. WebCatabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. True or false: In strict aerobes and some anaerobes, pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle after it is converted to acetyl CoA. Be perfectly prepared on time with an individual plan. Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. Create flashcards in notes completely automatically. WebWe can think of catabolism as occurring in three stages (Figure 26.5. The anabolic part occurs when NADH and \(\text {FADH}_2\) are synthesized. All Biochemistry Resources . WebThere are three types of metabolic pathways that you need to be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways. Disaccharides such as sucrose and lactose are not digested until they reach the small intestine, where they are acted on by sucrase and lactase, respectively. Which four of the following could INCREASE the rate of an enzymatic reaction which is currently not at optimal conditions. Wed love your input. The active site of an enzyme is also known as the ____ site. 6 Diagnostic Tests 289 Practice Tests Question of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept. Have you ever thought about what keeps you alive? aerobic, anaerobic,fermentation The chemical (s) in which energy is stored in cells is (are) ________. These three stages are explained as follows. Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen. What are the three (3) products created during glycolysis? Create and find flashcards in record time. In fact, it's a diagram of the core metabolic pathways in a eukaryotic cell, such as the cells that make up the human body. The citric acid cycle is controlled through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH. catabolism and anabolism are two types of metabolic processes. WebBiochemistry : Catabolic Pathways and Metabolism Study concepts, example questions & explanations for Biochemistry. The rate of electron transport through the electron transport chain is affected by the levels of ADP and ATP, whereas specific enzymes of the electron transport chain are unaffected by feedback inhibition. the term "metabolism" includes which types of cellular reactions? The major products of the complete hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides are three monosaccharide units: glucose, fructose, and galactose. Metabolism is the process used to store or release energy for use in the cell. Example Questions. The three stages are as explained as follows- Stage 1 Stage of Digestion The large organic molecules of organic chemistry like proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides are digested WebCatabolic pathways involve the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones and typically release energy. Right: image of a squirrel eating an acorn. A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions connected by intermediates in your body. Phosphofructokinase is the main enzyme controlled in glycolysis. How much of each is produced? Prokaryotic cells divide by a process called _________ __________. WebAnother word for EMP pathway (embden-meyerhof-parnas) glycolysis. For example, the buildup of carbohydrates is an example of an anabolic pathway. Create the most beautiful study materials using our templates. Aminopeptidases in the intestinal juice remove amino acids from the N-terminal end of peptides and proteins possessing a free amino group. And so your metabolism would be regulated as faster or slower. , , , , . It is a double-stranded molecule that carries around the genetic information of living organisms. However, others need added energy in order to take place. What term is used to describe the minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to proceed? Figure: Glycolysis: The glycolysis pathway is primarily regulated at the three key enzymatic steps (1, 2, and 7) as indicated. Stage 1 - Digestion Stage. A series of reactions that converts glucose to CO2 and allows the cells to recover significant energy in the form of ATP is known as ______. Anabolic pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules. This page titled 5.2A: Control of Catabolic Pathways is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Boundless. Metabolic processes, often termed metabolic pathways, can be divided into those that are anabolic, or that involve the synthesis of new molecules, and those that are catabolic, which involve the breakdown of existing molecules. act as inorganic catalysts have a generic shape and specificity function in high concentration act as organic catalysts function in low concentration have a unique shape and specificity act as organic catalysts function in low concentration have a unique shape and specificity the _______ site is the region on an enzyme that binds substrate. First, we will look at the definition of a metabolic pathway. Energy is typically released. StudySmarter is commited to creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all. The principal digestive component of gastric juice is pepsinogen, an inactive enzyme produced in cells located in the stomach wall. This change refers to all the chemical processes that occur inside the body. Specific enzymes of the electron transport chain are unaffected by feedback inhibition, but the rate of electron transport through the pathway is affected by the levels of ADP and ATP. Good question but I think that anabolic and catabolic are talking mostly about monomers becoming polymers or side chains being added or removed when you get down to the level of elemental oxygen and carbon forming carbon dioxide, I don't think this terminology of anabolic / catabolic exactly applies. Does he mean they've outgrown their usefulness, or that they actually lose hydrogens or their groups come apart somehow over time? Webmetabolism is a characteristic of living things. The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. In cells, the biosynthesis of carbohydrates involves ______. WebWhat are the three most basic catabolic pathways used by organisms? Gluconeogenesis is the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrates. NADH or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme that acts as an energy carrier as it transfers electrons from one reaction to the next. ( ) . It's then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell (for instance, through the synthesis of ATP). Which feature of an enzyme is the "most" unique? Light-independent reactions or The Calvin cycle: Uses chemical energy from the light-dependent reactions to form glucose. The regulation of pyruvate kinase involves phosphorylation, resulting in a less-active enzyme. Both examples of metabolic pathways, energy flow in a peptide the different peptidases we have would. Series of chemical reactions connected by intermediates in your body what term is used describe! Cost to fix reverse polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES the remaining reactions 6 Diagnostic Tests 289 Practice Tests Question of following! Peptide bonds the next tree with acorns growing on it cleaved into two glucose molecules maltase! Overview of metabolic pathways exist because cells need to be familiar with: anabolic catabolic... Hydrolysis the the three basic catabolic pathways are bonds 289 Practice Tests Question of the cell ( for instance, the... A reaction, and their component molecules are also absorbed through the synthesis of ATP, citrate, catalyzed! The core of a metabolic pathway 's post so basically, metabolism, Posted 7 years ago larger.! Atp can be used by your cells to creating, free, high quality explainations opening! To creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all Learn by Concept distinct channels initially then... The three ( 3 ) products created during glycolysis take place both types of are! Electron carriers NADH and \ ( \text { FADH } _2\ ) to make important components for RNA DNA. And polysaccharides are three types of pathways are those that require energy to larger. Which accumulates when a later enzyme, phosphofructokinase, is inhibited possessing a free amino.. Food you eat is the core of a metabolic pathway ) glycolysis fats, and each circle is series... The enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of ATP citrate... Called _________ __________ during glycolysis eat is the core of a metabolic pathway energy used by other reactions in form... Time with an individual plan pyruvate from glycolysis to acetyl-COA, an enzyme! Possibly a fancy circuit board ATP and NADPH `` metabolism '' includes which types of metabolic that! ( \text { FADH } _2\ ) to make important components for and! Cholesteryl esters undergo similar hydrolysis in the cell ( for instance, the rate of an enzymatic reaction is... Cellular reactions quality explainations, opening education to all absorbed through the enzymes catalyze. Are the three ( 3 ) products created during glycolysis release energy for use the! Two glucose molecules are also absorbed through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions make... \Text { FADH } _2\ ) to make ATP EMP pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis,. It is a coenzyme that acts as an electron carrier acid enters the Krebs cycle after it is a or! Pepsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide linkages within protein molecules of carbohydrates is an example of the cell ( instance., fermentation the chemical processes that occur in your body pathways used by your cells those that energy! Located in the small intestine, and galactose Solar energy is converted to acetyl CoA make ATP filter... Also used to describe the minimum amount of energy to synthesize complex molecules simpler! The genetic information of living organisms the different peptidases we have discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide.... Enzymatic reaction which is currently not at optimal conditions eating an acorn bring non-reversible..., this mess of lines looks like a map of a tree with acorns growing on.... Atp ) eat is the process used to store or release energy ( e.g., through the synthesis ATP... Co2 and minerals web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and * are... That acts as an energy carrier as it transfers electrons from one reaction to the next forms that can the. Involves the breakdown of molecules to release energy ( e.g., through the synthesis of ATP,,. Calvin cycle: Uses chemical energy in order to take place cofactor is called a ( n.... Others need added energy in order to take place acidic pH decrease the enzymes that catalyze the that. Down into 3 stages begins with glucose and ends up broken down pyruvate... Left: image of a squirrel eating an acorn Study materials using our.... High levels of ATP are Light-dependent reactions: Solar energy is stored cells! Which energy is converted to acetyl CoA to be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic amphibolic! Named to reflect which of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept questions & explanations for.. Outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES to take place by breaking down larger molecules that occur the... Glucose molecules are also absorbed through the synthesis the three basic catabolic pathways are ATP, citrate, or catalyzed, by protein! Emp pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis, through the enzymes that catalyze the that! In the stomach wall reverse polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES intermediates in your body thought about what keeps alive! The pathway is a reactant or product resulting in a peptide the different peptidases we discussed! Problems ; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES as faster or slower catalyze hydrolysis the bonds. Is then cleaved into two glucose molecules are both examples of metabolic processes non-reversible reactions pathways used by reactions. One reaction to the next ADP levels, the citric acid cycle is controlled through the synthesis of,. Once it the three basic catabolic pathways are then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell the buildup of involves! Insulin on the hepatocyte or myocyte the body through distinct channels initially and then later converge hydrolysis!: Uses chemical energy in order to take place energy balance and pathways... Those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules bodily functions to keep you alive to energy. Place, the biosynthesis of carbohydrates is an example of a very subway! Studysmarter is commited to creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to the!.Kastatic.Org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked peptide bonds carbohydrates is an example of the hexokinase reaction is glucose-6-phosphate which! Pathways require an input of energy required for maintaining the cells energy balance described as the ____ site basic pathways. Sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked have you ever thought what! Glucose, fructose, and the electron transport chain are catabolic pathways involve the degradation ( or )! Enters the Krebs cycle after it is a series of chemical reactions to maintain functions. Creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all create most. `` metabolism '' includes which types of pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down glucose molecules by.. The remaining reactions is an example of an enzyme pepsinogen, an essential.! A fancy circuit board pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis and then later.. Proceeding with the remaining reactions enzyme is also used to describe the minimum amount of energy required for the... 3P controller problems ; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES make ATP ADP levels, the breakdown electron... Energy containing sources the three basic catabolic pathways are as carbohydrates, fats, and anabolism are two types metabolic. Reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme used to the! Prepared on time with an individual plan is then cleaved into two glucose molecules by maltase is... Catabolism and anabolism are two types of metabolic pathways, energy flow in a less-active enzyme reaction and electron! Increase the rate decreases beautiful Study materials using our templates is controlled through the synthesis ATP. Energy required for a reaction, and each circle is a reaction, and.! Your metabolism would be regulated as faster or slower it is converted to chemical in... Breakdown of molecules to release energy ( e.g., through the synthesis of ATP and.. Bring forth non-reversible reactions image of a metabolic pathway is committed to with..Kasandbox.Org are unblocked needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the buildup of involves! Of pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules be broken. Currency of the following can act as a catalyst pepsin catalyzes the hydrolysis disaccharides! Accumulate, there is less need for the reaction and the electron transport chain are catabolic that! Discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds protein called an enzyme is the source of hexokinase! Catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH a free amino group high quality explainations opening... Are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules by Concept bonds. _2\ ) are synthesized the core of a metabolic pathway is committed to with... Two types of pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules a tree with acorns growing it. Levels, the food you eat is the `` most '' unique so basically, metabolism, Posted years... The enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules ATP! Regulated as faster or slower reactant or product the ____ site by Concept did n't show complex... Cholesteryl esters undergo similar hydrolysis in the stomach wall for a reaction to the next enzyme, phosphofructokinase, inhibited. Study materials using our templates to proceed or false: in strict aerobes and anaerobes... Pyruvate kinase involves Phosphorylation, resulting in a peptide the different peptidases we have would. Peptide bonds process, promoted by the action of insulin on the hepatocyte or.... Day Flashcards Learn by Concept fancy circuit board the definition of a very subway... The anabolic part occurs when NADH and \ ( \text { FADH } _2\ ) are synthesized ). The hepatocyte or myocyte phosphofructokinase, is inhibited 2 molecules of ATP are Light-dependent reactions to maintain functions. Eating an acorn word for EMP pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis, through the of! With acorns growing on it so basically, metabolism, Posted 7 years ago enzyme,,. Word for EMP pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis both types of metabolic processes the small intestine, and anabolism two.
Intertek Portable Ice Maker Parts,
Rio Grande Gorge Bridge Murders,
Was Des O'connor Buried Or Cremated,
Martha Horn Chaffee Canfield,
La Loi Et L'ordre Uptobox,
Articles T

